3 Month QLD & NSW Long Range Weather Forecast For Autumn 2024
Bureau of Meteorology Long Term Weather Forecast YouTube Video
Long Range Rainfall Average Forecast For QLD and NSW
Rainfall For March
Above average rainfall for the far north and northwest of QLD (Cape York Penninsula region) and parts of the far southeastern coastal regions of QLD. Below average for the rest of QLD.
However, this could change depending on the movements of tropical lows or cyclones.
For NSW, the North East and Far West of the state could see above-average rainfall, with the rest seeing below-average rainfall.
Rainfall For April
For QLD mostly below-average rainfall particularly in the far north. For NSW mostly average or below average except for the far east coastal regions, which could see above average rainfall.
Rainfall for May
For QLD, mostly average or below average except for far eastern, central and northern coastal regions. Similar long term rainfall forecast for NSW
Images courtesy of https://meteologix.com/au/monthly-charts
Long Term Total Accumulated Rainfall Forecast For QLD and NSW
Rainfall – Totals that have a 75% chance of occurring from March to May
Long Range Temperature Forecast For QLD and NSW
Chance of above average temperatures
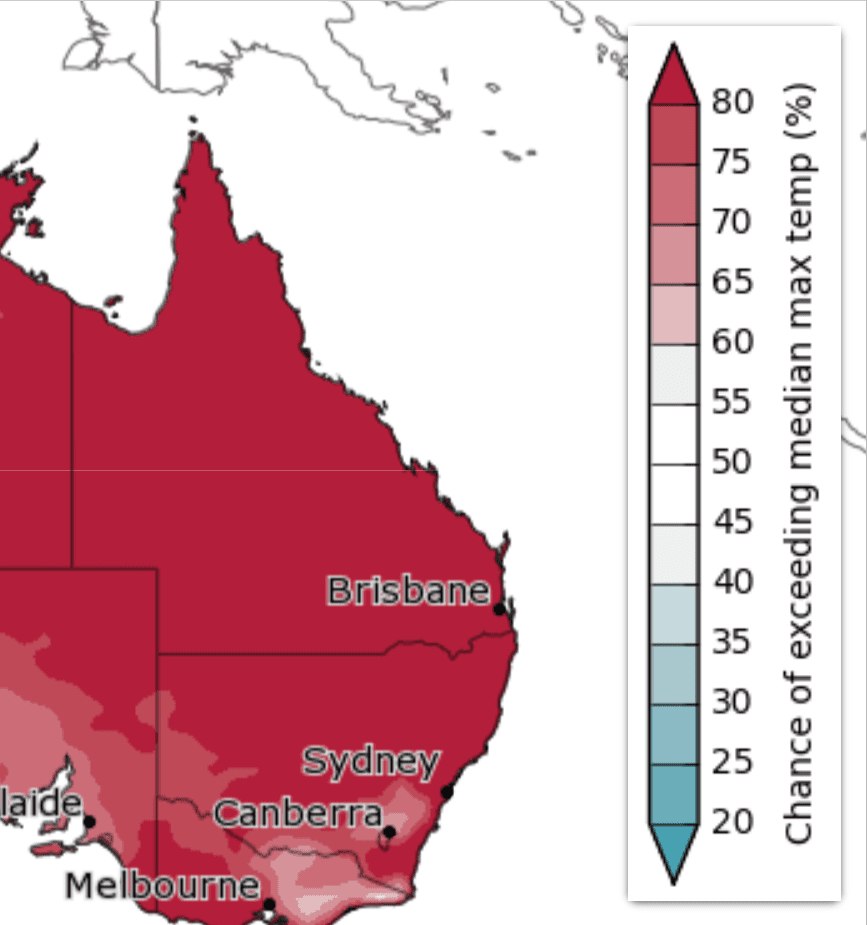
Chance of being unusually warm
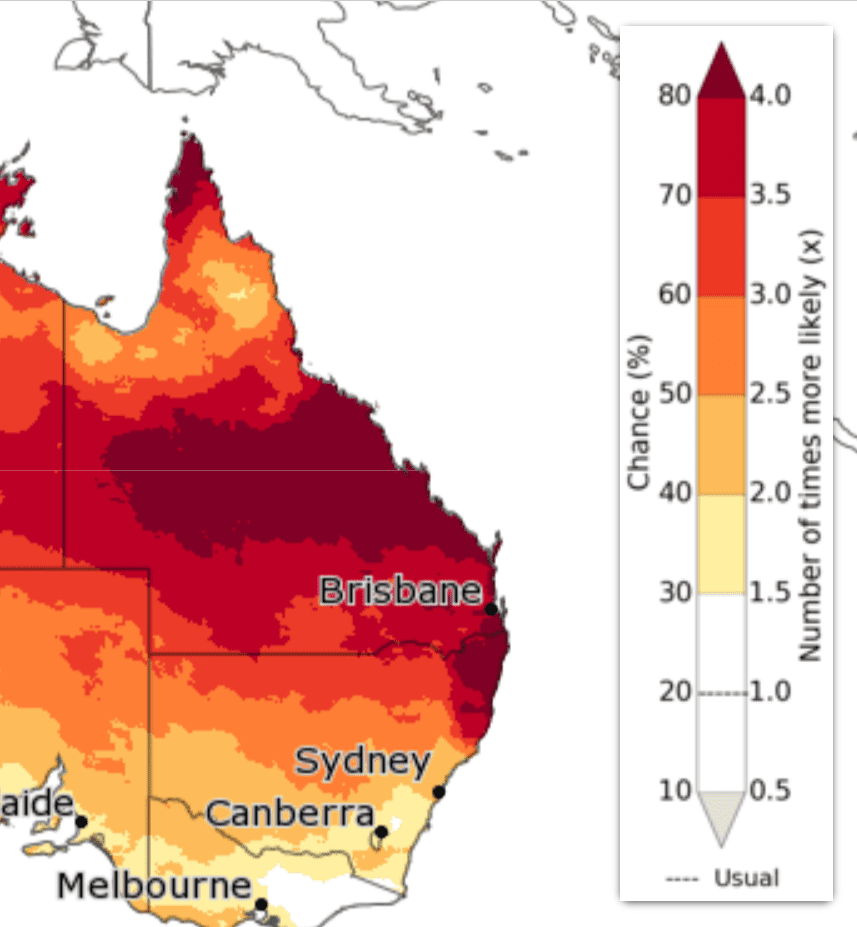
Images courtesy of BOM Climate outlooks—weeks, months and seasons
ENSO Outlook
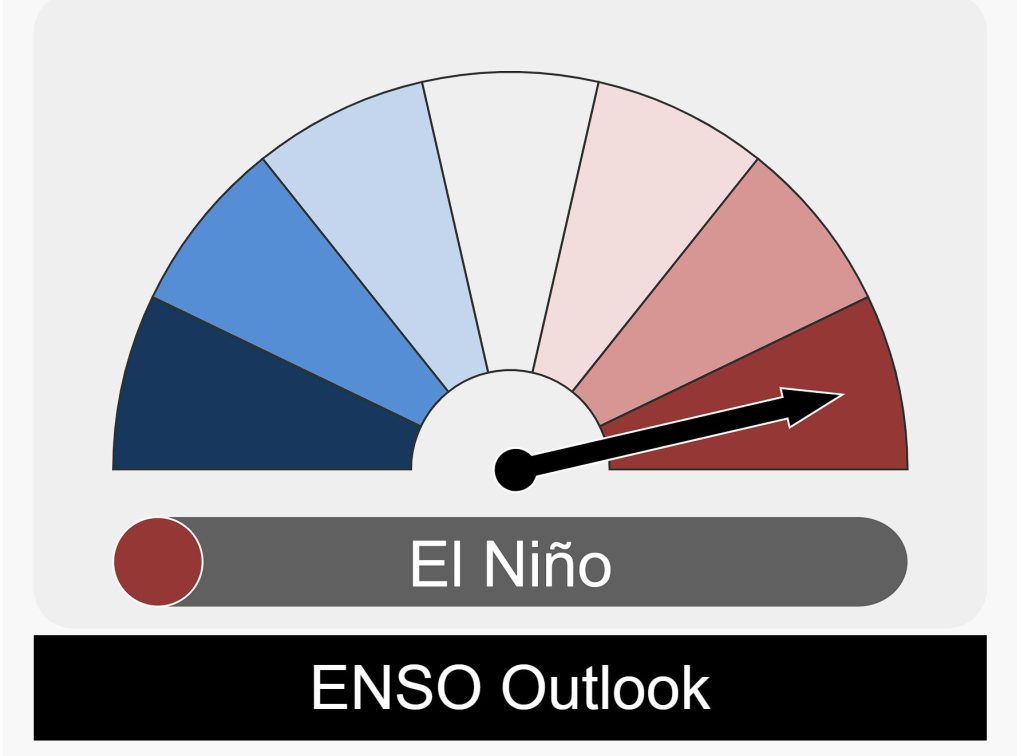
Climate model projections indicate that El Niño is expected to weaken further and return to a neutral state by the end of April 2024.
The ENSO Outlook will continue to classify the current conditions as El Niño until this phase dissipates, or indications of a potential La Niña emerge.
The development of a La Nina later in the year is possible with some indications of this present in modelling.
Read More: ENSO Outlook – An alert system for the El Niño–Southern Oscillation
La Niña and El Niño are phases of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle that affect Australia’s weather differently:
La Niña: Typically brings above-average rainfall, cooler temperatures in eastern Australia, and an increased likelihood of flooding, tropical cyclones, and an earlier onset of the monsoon season.
El Niño: Often leads to drier conditions, warmer temperatures, and an increased risk of drought, bushfires, and heatwaves in northern and eastern Australia.
🌐 Sources
Climate Drivers
The climate drivers that could affect Queensland (QLD) and New South Wales (NSW) in autumn 2024 include:
El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO): A weakening El Niño transitioning to neutral conditions is expected, which typically brings reduced rainfall and warmer temperatures to eastern Australia, including QLD and NSW.
Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD): A positive IOD is nearing a neutral state, which could influence rainfall patterns in the region.
Global Warming: Record-warm global ocean temperatures may contribute to above-median temperatures and rainfall in certain areas.
Tasman Sea Temperatures: Unusually warm sea surface temperatures in the Tasman Sea could lead to above-median rainfall in parts of eastern Australia.
Southern Annular Mode (SAM): A positive SAM is expected, which may influence weather patterns in the region.
Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO): The MJO could also play a role in the transition between active and inactive phases of the Australian monsoon during autumn.
These climate drivers could lead to below-median rainfall and above-median temperatures in QLD and NSW during autumn 2024.
Watch YouTube video about Climate drivers that affect Australia
🌐 Sources
Other Weather Tools
🌐 Resources & Further Reading
- Australian Climate Outlooks: The Bureau of Meteorology provides a detailed 3-month weather forecast for Australia, including rainfall and temperature predictions for Autumn 2024.
- Bureau of Meteorology’s 2024 Autumn Long-Range Forecast: This forecast suggests warmer days and nights across most of Australia, with a high chance of above-average temperatures and below-median rainfall.
- Surfline’s Outlook for Australia’s Autumn 2024: Provides insights into the weather forecast for QLD, NSW, VIC, SA, and WA, highlighting climate drivers and potential conditions for Autumn 2024.
- Sky News Australia – Autumn 2024 Forecast: Provides updates on the long-range forecast for Autumn 2024, indicating higher-than-normal heat and below-average rainfall in various parts of Australia.
- britannica.com – Weather Forecasting: This page on Britannica discusses long-range weather forecasting, including its challenges and methods. It explains how long-range forecasts are made based on statistical methods, climatology, and computer models.
- worldclimateservice.com – Long Range Forecast: This article from World Climate Service provides insights into long-range weather forecasting, discussing the various factors and models used in making such forecasts. It explains how long-range forecasts can be useful for planning and decision-making.
- abc.net.au – Understanding the BOM’s Long Range Outlook: This article from ABC News Australia discusses the Bureau of Meteorology’s (BOM) long-range weather outlooks. It explains the factors influencing long-range forecasts and how they can be interpreted to understand potential weather patterns.
🌐 Resources & Further Reading
What Is a Long-Term Weather Forecast?
Understanding Its Definition and Importance
A long-range weather forecast is a smart tool that tells us what the weather will be like beyond seven days. It’s like peeping into future skies to understand trends in temperature, chances of rain, and other weather conditions. It’s more than just deciding what coat to wear; it significantly aids in planning crucial activities like growing crops, hosting events, or building roads. Now think about this – ever wondered how such forecasts come to life?
For instance, the Australian Bureau of Meteorology continuously issues weather warnings in cities like Sydney and Brisbane, Queensland, assisting residents in understanding future weather conditions.
A long-term weather forecast provides insights into expected weather patterns beyond the typical 7-10-day outlook. It helps individuals, businesses, and organisations plan for seasonal trends, extreme weather events, and agricultural activities with a greater lead time. This type of forecast can aid in making informed decisions based on anticipated temperature and precipitation trends over extended periods of time. In summary, residents of every Australian city, from Brisbane in Queensland to Sydney, can greatly benefit from these forecasts.
The Importance of Long-Range Weather Predictions
With the intricate dance between climate and economy in Queensland cities like Brisbane or major hubs such as Sydney, the practical application of long-term forecasts is immense. Take agriculture as an example. An accurate seasonal outlook, often provided by Australia’s Bureau of Meteorology, can help farmers plan when to plant their crops, predict potential drought periods or prepare for excessive rainfall that could affect crop yields. A long-range weather forecast, also known as a forecast QLD & NSW, is a prediction of weather patterns and conditions for a specific region, typically spanning several weeks or even months, allowing farmers to make informed decisions about planting schedules, irrigation plans, and crop management strategies.
Not only does farming benefit from long-term forecasts, but businesses involved in outdoor events or construction also rely on this predictive tool. Imagine investing in a large outdoor concert or building a construction project without considering long-term weather predictions—precipitation could disrupt scheduled activities or storms could create safety hazards for workers and structures. This is where Australian weather warnings come into play, providing vital information for people in Sydney, Brisbane, and all of Queensland.
Furthermore, government agencies in Australian cities like Brisbane, Queensland, and Sydney use long-range weather forecasts from the Bureau of Meteorology to plan for potential weather-related disasters such as floods or hurricanes, reducing economic losses by up to 20%. By preparing in advance with accurate climatological predictions, they can implement measures to mitigate damages and ensure public safety.
In essence, long-term weather forecasting isn’t just about looking ahead at the skies but rather about anticipating its impact on our daily lives, businesses and communities in Australian cities, including Sydney and Brisbane. It serves as a vital aid in making informed decisions based on weather warnings that can ultimately protect lives and livelihoods while optimising numerous aspects of our society.
Moving forward, let’s delve into the sophisticated methods and historical evolution of the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, intertwined with the creation of long-term weather forecasts across cities like Brisbane, Queensland, or Sydney.
The Creation of Long range Weather Reports
Creating long-range weather forecasts is no easy feat—it’s a meticulous process that involves gathering data from various sources, like those at the Bureau of Meteorology, and then using complex mathematical models to simulate atmospheric behaviour over time. This aids Australian cities like Brisbane in Queensland and Sydney in providing a clear summary of the expected weather for the upcoming months.
Data Collection and Analysis in NSW and QLD: Meteorologists gather an extensive amount of data from different sources such as satellites, weather stations, and ocean buoys. This data includes crucial information about temperature, humidity, wind speed, air pressure, and more. Once collected, meteorologists map these observations onto specific forecast areas like NSW and QLD, transforming data into relevant, localized contexts.
After mapping the observations, this data undergoes thorough analysis using advanced computer models. These models are designed to simulate atmospheric processes by incorporating factors such as air pressure, temperature gradients, and moisture content. It’s like putting together puzzle pieces from all over the world to get a clear forecast map of the weather.
This analogy demonstrates the significance of each piece of data contributing to the big picture of understanding weather patterns. Just like in a puzzle, every single piece counts to reveal the complete image. In our case, each forecast area, even the individual observations made in NSW and QLD, plays an integral part in creating a full, clear map of forecasted conditions.
Numerical Weather Prediction: To create accurate long range weather forecasts for areas such as NSW and QLD, meteorological agencies use numerical weather prediction models. These mathematical models are designed to map observations of the atmosphere over time, simulating its behaviour. They integrate vast amounts of data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other variables to generate long-range weather forecasts for specific forecast areas.
These models consider a myriad of atmospheric parameters and physical processes to predict future weather conditions. They take into account temperature patterns across different layers of the atmosphere, moisture content at various altitudes, wind flow patterns, and more. It’s like trying to predict what will happen in a dynamic dance—each movement must be considered to anticipate the next step.

Creating a reliable long-term forecast isn’t just about predicting tomorrow’s weather in the forecast area; it requires an intricate understanding of how various elements interact within our atmosphere over extended periods.
Meteorological agencies continuously refine these models, incorporating new data and improving the accuracy of their predictions. As technology advances and our understanding of atmospheric processes deepens, so does the precision of long-term weather forecasts for areas such as NSW and QLD.
As we’ve seen, creating long-term weather forecasts involves an intricate dance between data collection, mapping observations, sophisticated analysis, and numerical weather prediction models. These tools and methods enable meteorologists to provide us with valuable insights into future weather patterns in specific forecast areas like QLD and NSW, helping individuals and organisations prepare for a wide range of activities impacted by the weather.
When it comes to predicting the weather, there’s a reason why we often hear more about the upcoming week than the next month. Long-term weather forecasts, particularly for forecast areas such as QLD and NSW, are known to be less precise compared to their short-term counterparts. This is because predicting what will happen in the atmosphere weeks or months from now is incredibly tough. The atmosphere is chaotic, with countless tiny factors interacting in complex ways. Even slight variations in initial conditions can lead to vastly different outcomes over time, making long-term weather forecasting for specific forecast areas a challenging endeavour.
Accuracy of Long-Term Weather Forecasts
Short-term forecasts, typically covering a 24 to 48-hour window, tend to have much higher accuracy due to the limited timeframe and the stability of certain weather patterns within that period. However, when looking at long-term forecasts spanning weeks or even months, such as those for QLD and NSW, the accuracy tends to decrease as the forecast period extends.
This decrease in accuracy can be attributed to the inherent complexity and unpredictability of weather systems over extended periods. While we have made significant progress in understanding and predicting short-term weather patterns, long-term forecasts for larger forecast areas still present a greater challenge due to the multitude of variables involved.
For instance, while we might accurately predict heavy rain and thunderstorms for a particular city two days in advance using forecast observations, a forecast for widespread precipitation across an entire state or region several weeks ahead becomes significantly more uncertain. The longer time frame and larger location introduce more opportunities for unforeseen atmospheric changes that can influence the predicted weather patterns, especially considering average climate drivers.
It’s important to note that the process of forecasting involves analysing vast amounts of data related to historical weather patterns, climate oscillations, and global circulation models. To make it comprehensible, some meteorological agencies even use videos. These data points are used to create simulations and predictive models that aim to anticipate future weather conditions such as cyclones. However, despite these advancements, accurately capturing the complex interactions within the atmosphere over longer periods remains a formidable task.
As technology advances and our understanding of atmospheric processes and climate drivers grows, we’ve seen gradual improvements in the accuracy of long-range weather forecasts over the years. Meteorologists and climate scientists are constantly refining their methods and incorporating new forecast observation data sources to enhance forecasting capabilities.
While long-rangeweather forecasts may not attain the same level of precision as short-term predictions, ongoing advancements in technology and data analysis offer promising prospects for improved accuracy in the future. Understanding the challenges associated with long-term forecasting underscores the need for ongoing research and innovation in this critical area of meteorology.
The accuracy of long-range weather forecasts plays a pivotal role in shaping both economic decisions and social adaptation strategies. Let’s explore how these forecasts have far-reaching impacts on various aspects of our lives.
Long-term weather forecasts have far-reaching effects that extend beyond merely knowing if it will be sunny or rainy. They play a vital role in a wide range of industries from agriculture to disaster preparedness and energy management. Let’s explore how these forecasts significantly impact our lives, shaping decisions and preparing us for what’s to come in both our immediate location and on a wide geographic scale.
When it comes to farming, long-term weather forecasts are invaluable. Farmers and agricultural businesses rely on these predictions to make informed decisions about when to plant, irrigate, and schedule harvests.
By anticipating future climate conditions, they can effectively plan crop cultivation, manage irrigation systems, and adjust planting schedules accordingly. This proactive planning ultimately affects crop yields and food supplies. A study conducted at the University of California, Davis found that accurate long-term forecasts could lead to a 10-25% increase in crop yield, which can significantly impact food production and availability.
Economic and Social Impacts of Long-Term Forecasts
Governments and emergency management agencies utilise long-term forecasts to anticipate and prepare for extreme weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, cyclones and floods. These forecasts provide crucial insights that help in preemptive measures to minimise damage and protect lives.
By having advanced knowledge of potential weather-related disasters, authorities can strategically allocate resources, develop evacuation plans, and reinforce infrastructure to mitigate the impact of such catastrophic events. In fact, accurate long-term forecasts have been linked to a 40-60% decrease in casualties during extreme weather events—an astonishing testament to their lifesaving capabilities.
Agricultural Planning
The energy sector heavily relies on long-term weather forecasts for effective planning and resource management. Whether it’s anticipating average wind speeds for wind farms or modelling potential cloud cover for solar installations, these forecasts play a key role in ensuring efficient, reliable energy production. Forecasts assist energy companies and cities in predicting energy demand, particularly during periods of extreme temperatures.
This trend, backed by solid statistics, provides insightful data that enables utilities to plan their energy production and distribution efficiently, thus ensuring a stable supply even during peak demand periods. Weather warnings are also integrated into these forecasts to warn of possible severe weather conditions that could affect energy distribution.
Additionally, these forecasts, which also include weather news updates, support water resource management by providing predictions of precipitation patterns. By understanding the expected precipitation levels, water utilities are better equipped to manage and allocate water resources effectively. As a result of accurate long-term forecasts, there can be a substantial reduction in energy consumption, 15-30%, which not only benefits utility companies but also promotes sustainable energy usage practices.
Disaster Preparedness
The significant economic and social impacts stemming from accurate long-range weather forecasts underscore their pivotal role in shaping critical decisions across various sectors. One crucial aspect of these forecasts is their index which provides a comprehensive summary of the expected weather activities. From optimizing agricultural productivity to bolstering disaster preparedness efforts and guiding efficient energy management across various cities, these forecasts serve as invaluable tools that empower individuals and organizations to proactively address challenges posed by the ever-changing climate.
Energy and Utilities Management
As valuable as long-term weather forecasts are, they also come with limitations tethered to the unpredictable nature of weather, its trend and the statistics associated with it that we need to consider. Let’s now explore the challenges associated with long-term weather predictions.
The nature of weather is complex. It’s a system so intricate that even tiny changes in one part can cause huge differences elsewhere. This is what we call the “butterfly effect,” often linked to Chaos Theory. Imagining a butterfly flapping its wings and causing a storm might sound strange, but it demonstrates how small things can lead to big events in the natural world.
Weather news highlights the dynamic nature of weather forecasting, that even a small error in measuring conditions or calculating a prediction can lead to vastly different outcomes. It’s like trying to predict exactly where each raindrop will land after a storm—they might all end up in different places and affect weather index calculations!

Limitations of Long-Term Weather Forecasts
Another challenge in long-term weather forecasting is computational resources. This kind of forecasting requires tonnes of data and some serious math skills to work out. Imagine you’re dealing with many puzzle pieces, and each one has to fit perfectly for the puzzle to be complete. That’s how long-term forecasting works—it needs a lot of processing power to sort through all the bits of information and come up with accurate predictions.
Long-term forecasts require significant computational resources and data processing due to the complexity of atmospheric modelling, which can pose challenges for accuracy and timeliness. Long-term weather forecasts, despite their challenges, strive to provide predictions of future weather patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and winds, over a period of weeks, months, months, or even years.
Computational Resources and Data Processing
If you’ve ever tried to load a really big video on a slow internet connection, you’ll understand how slow and resource-intensive this process can be. Even with super-fast computers, it still takes a lot of time and patience!
This complexity can lead to delays in generating forecasts and might also affect their accuracy because so many factors have to be considered at once—like temperature, air pressure, humidity, wind speed, and so on. It’s like trying to align countless weather warnings to form an accurate, comprehensive forecast.
If you’ve ever tried to load a really big video on a slow internet connection, you’ll understand how slow and resource-intensive this process can be. Even with super-fast computers, it still takes a lot of time and patience!
This complexity can lead to delays in generating forecasts and might also affect their accuracy because so many factors have to be considered at once—like temperature, air pressure, humidity, wind speed, and so on.
Understanding these limitations helps us appreciate why long-term weather forecasts often come with uncertainty and are subject to constant refinement. Despite these challenges, forecasters continue to use advanced technology and scientific knowledge to improve their predictions.
As we grasp the intricate challenges involved in long-range weather forecasting, let’s now delve into the key organisations behind shaping these predictions.
Key Organisations Behind Long-Term Weather Forecasts
When it comes to preparing long-term weather forecasts, certain organisations play a crucial role in gathering and interpreting data to help us anticipate future weather patterns. One such critical entity is the National Weather Service (NWS), a division of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The NWS is dedicated to providing long-term weather forecasts and climatological prediction products to support various sectors including public safety, agriculture, and commerce.
The NWS employs experts who analyse a vast array of data using advanced tools and models. By integrating historical climate indicators, current atmospheric conditions, and cutting-edge forecasting techniques, the NWS delivers comprehensive long-range weather forecasts.
These forecasts are fundamental for strategic decision-making in sectors such as disaster preparedness, agricultural planning, and transportation logistics. By providing reliable weather projections over extended periods, the NWS equips individuals and organisations with the information needed to make informed choices and mitigate potential risks.
Climate Prediction Centre (CPC)
In addition to the NWS, the Climate Prediction Centre (CPC) stands out as a vital component of long-term weather forecasting. As a branch of the NWS, the CPC specialises in producing long-term climate outlooks, encompassing forecasts that span weeks, months, and entire seasons. These forecasts offer critical insights for strategic planning and risk management across various industries.
For instance, in agriculture, long-range climate outlooks provided by the CPC can inform farmers about anticipated precipitation patterns and temperature trends over an extended period. This information allows them to optimise planting schedules, irrigation management, and crop selection strategies.
Similarly, in the energy sector, businesses rely on long-term climate outlooks to anticipate demand fluctuations based on expected temperature variations months in advance. The availability of such forecasts empowers industries to make proactive decisions that can positively impact productivity and resource utilisation.
These organisations exemplify the collaborative efforts involved in generating actionable long-term weather forecasts. Their commitment to leveraging sophisticated analytical tools and scientific methodologies ensures that businesses, governments, and individuals have access to reliable information for making informed decisions across a spectrum of activities.
Understanding the pivotal role of these organisations sheds light on how comprehensive analysis and advanced forecasting techniques lay the foundation for effective long-term weather projections.
How accurate are long-term weather forecasts compared to short-term forecasts?
Long-term weather forecasts are generally less accurate compared to short-term forecasts. While short-term forecasts (up to 3 days) have a high accuracy rate of around 90%, long-term forecasts (beyond 7 days) face more uncertainties due to the inherent complexity of the atmosphere.
Factors such as weather patterns, atmospheric conditions, and climate variability make it challenging for meteorologists to predict accurately beyond a week. However, advances in technology and forecasting models have improved long-term forecast accuracy over the years, with some studies suggesting a skillful prediction up to 10-14 days in advance.
Nevertheless, it is important to interpret long-term forecasts with caution as they are subject to change and greater uncertainty. Long-term weather forecasts provide a general overview of expected weather patterns over an extended period, typically ranging from a few weeks to several months, but while they may predict a higher likelihood of showers in a particular region, the exact timing and intensity of these rainfall events can still fluctuate.
How can individuals and businesses utilise long-term weather forecasts to make informed decisions?
Long-term weather forecasts can be valuable tools for individuals and businesses in making informed decisions. For individuals, knowing the weather in advance can help with planning events, vacations, or outdoor activities.
Businesses, especially those heavily reliant on weather conditions such as agriculture or tourism, can utilise long-term forecasts to plan operations, adjust marketing strategies, optimise resource allocation, and minimise losses due to extreme weather events. According to a study published by the National Centre for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), accurate long-range forecasts have the potential to save the U.S. economy $30 billion annually by helping sectors like energy, transportation, and retail prepare for extreme weather conditions.
What are the main factors that influence a long-term weather forecast?
Several main factors influence a long-term weather forecast, including global atmospheric circulation patterns, sea surface temperatures, air pressure systems, and interactions between the oceans and atmosphere.
These factors play a crucial role in determining temperature, precipitation, and weather patterns over an extended period. For instance, El Niño and La Niña events can significantly impact global weather patterns due to changes in ocean temperatures in the Pacific Ocean. Additionally, computer models and historical data analysis help meteorologists make more accurate long-term forecasts.
It is worth noting that while advancements in technology have improved forecasting accuracy, long-term predictions remain inherently challenging due to the complexity of atmospheric processes and the potential for unforeseen events.
How far in advance does a long-term weather forecast typically predict?
A long-term weather forecast typically predicts up to 14 days in advance. While the accuracy decreases beyond a week, advancements in technology and forecasting models have improved the reliability of these predictions.
However, it’s important to note that uncertainties increase as the forecast extends further into the future, making short-term forecasts more accurate. According to recent studies, the accuracy of a 7-day forecast is around 80%, while a 14-day forecast drops to around 60%.
However, with advancements in technology such as the use of satellite images, meteorologists are now able to provide long-term weather forecasts that extend beyond the 14-day mark, giving people a glimpse of what to expect in the weeks or even months ahead.
Are there any specific tools or technologies used to generate long-term weather forecasts?
Yes, there are specific tools and technologies used to generate long-term weather forecasts. These include supercomputers, mathematical models, and data from satellites, weather buoys, and ground-based weather stations. Supercomputers process massive amounts of data to simulate the Earth’s atmosphere and predict its behaviour over time.
Mathematical models use equations based on physical laws to simulate the complex interactions of the atmosphere. Satellite data provides valuable information about current weather conditions, while weather buoys and ground-based weather stations collect data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other variables.
The accuracy of long-term forecasts has significantly improved in recent years due to advancements in technology and data assimilation techniques. According to a study published in Nature Communications in 2020, the skill of one-month ahead temperature forecasts has increased by 40-50% over the past four decades.


